EnviroBiomics.lnc
ACTINO Analytical Report How To Read The Report

EnviroBiomics.lnc
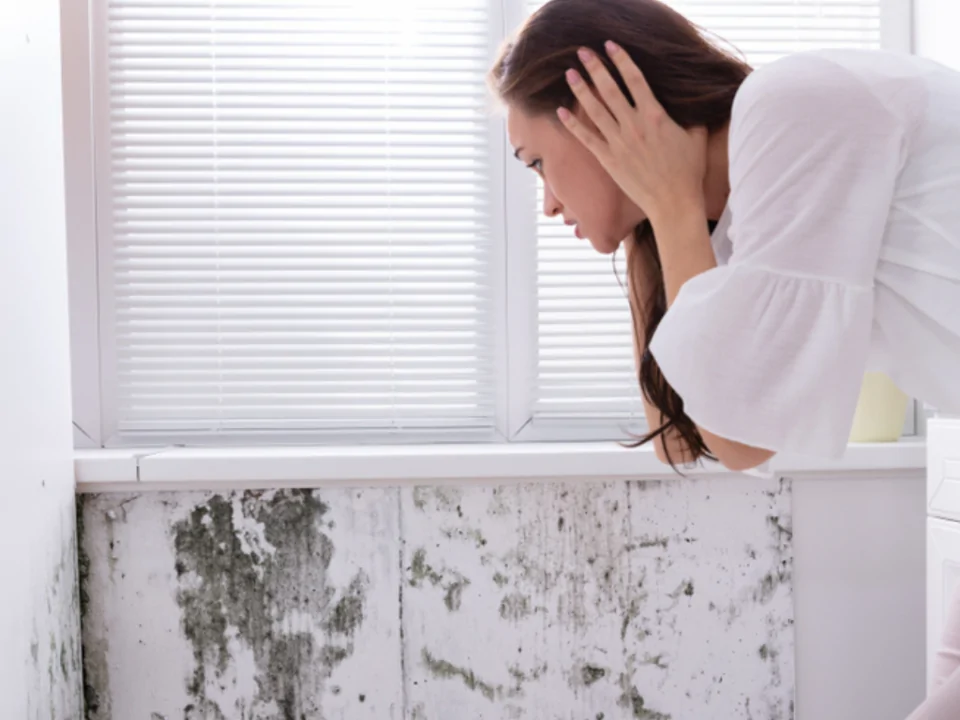
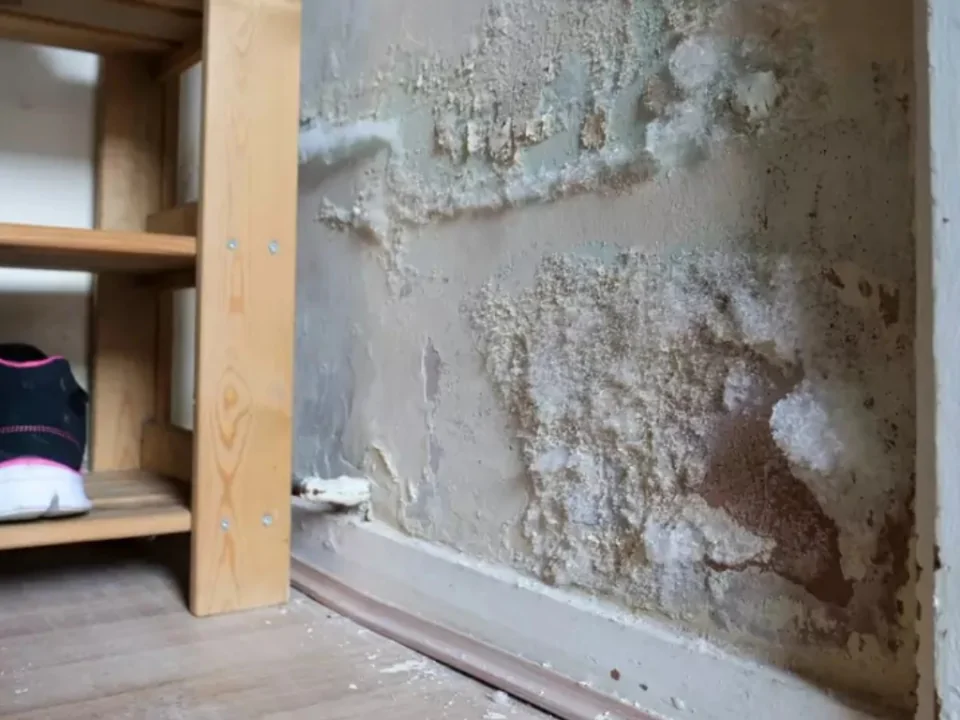
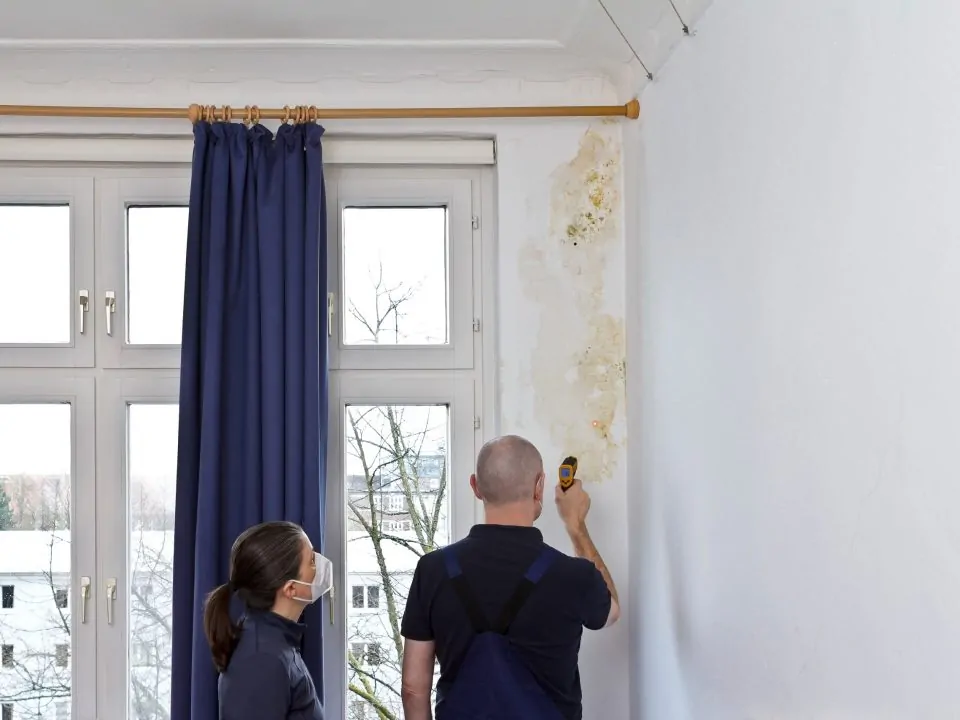
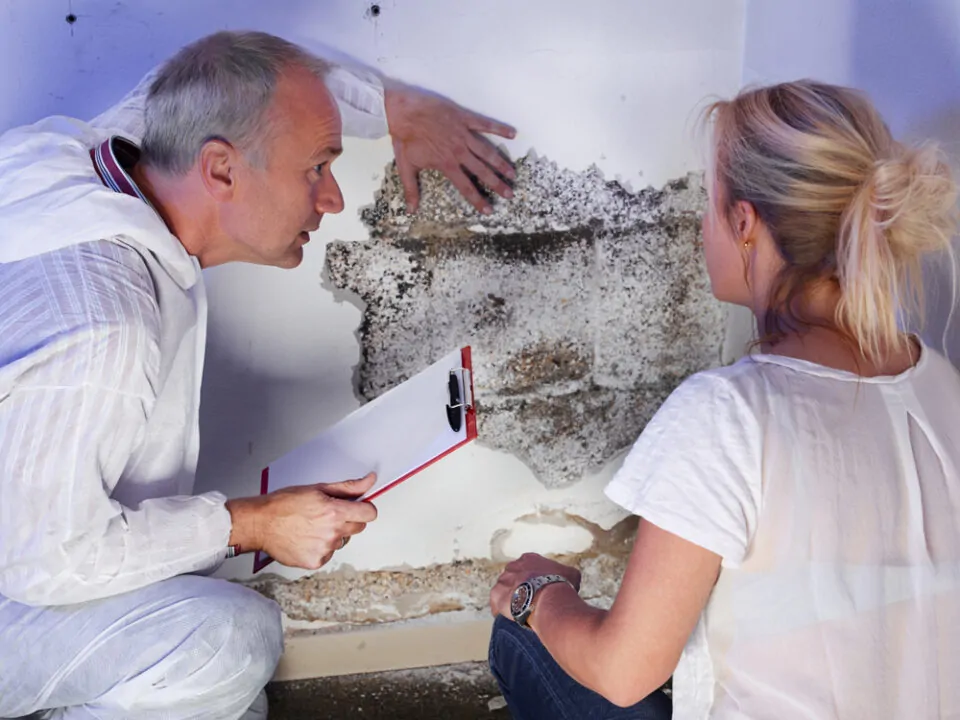
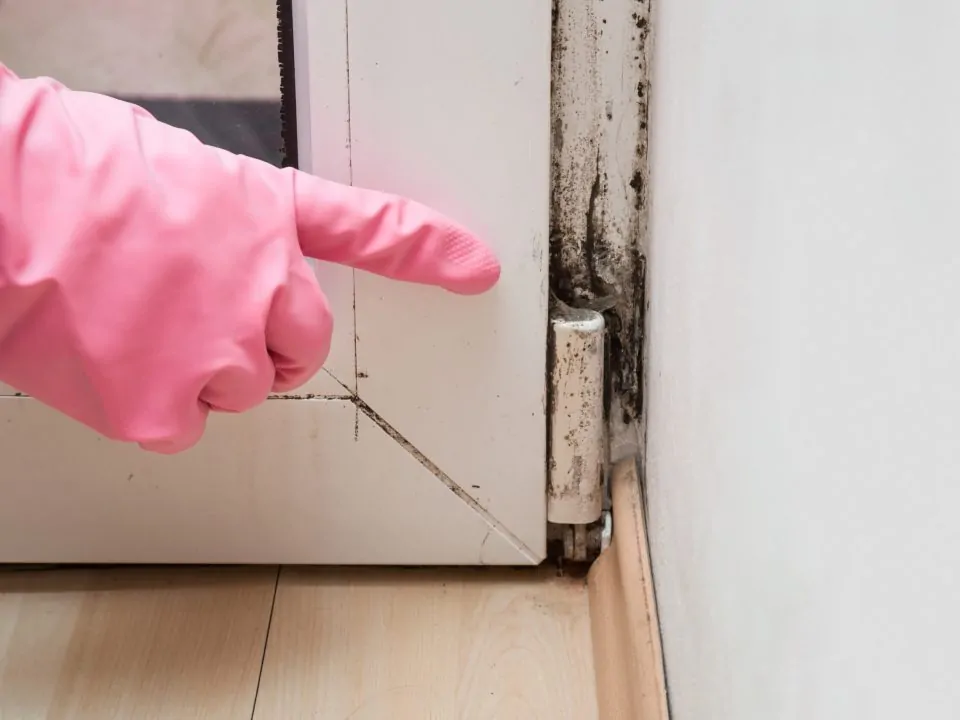
Keeping Your Family Free From Toxic Mold And Mycotoxins

EnviroBiomics.lnc
What is Human Bacteroides Test?

EnviroBiomics.lnc
How Familiar Are You With Indoor And Outdoor Allergens
Lab Services
Tests We Offer
Help Documents
Important information on the use of kits and references.
Our Services
Specialized Laboratory Tests
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory TestsMold Panels
Fusarium
Exophalia
Exerohelium
Scedosporium
Sporothrix
Trichoderma
Trichosporun
Custom orders
Laboratory TestsPeniciliums
Penicillium aurantiogriseum
Penicillium citreonigrum
Penicillium citrinum
Penicillium decumbens
Penicillium expansum
Penicillium glabrum
Penicillium oxalicum
Penicillium roquefortii
Penicillium sclerotiorum
Laboratory TestsFusarium
Fusarium solani f.sp. cucurbitae MP I
Fusarium solani f.sp. Batatas
Fusarium solani f.sp. mori MP III
Fusarium solani f.sp. xanthoxyli MP IV
Total fusarium
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory TestsAspergillus
Aspergillus terreus
Aspergillus carbonarius
Aspergillus flavipes
Aspergillus nomians
Aspergillus parasiticus
Aspergillus puniceus
Laboratory TestsW.H.O. Lists Top Fungal
Health Threats
Candida albicans
Candida auris
Cryptococcus neoformans
Aspergillus fumigatus
Laboratory TestsOthers
Emericella (Asp.) nidulans
Memnoniella echinata
Paecilomyces variotii
Trichoderma harzianum
Ulocladium botrytis
Exophiala dermatitidis
This technology has a plethora of applications, such as:
- diagnosing and understanding complex diseases.
- whole-genome sequencing.
- analysis of epigenetic modifications.
- mitochondrial sequencing.
- transcriptome sequencing understanding how altered expression of genetic variants affects an organism.
- Exome sequencing mutations in the exome are thought to contain up to 90% of mutations in the human genome, which leads to disease.
- DNA techniques have been used to identify and isolate genes responsible for certain diseases, and provide the correct copy of the defective gene known as ‘gene therapy’.
Latest Blog
What's New
Science-Based Environmental Testing Education
Learn from the Experts
CIRS Protocol
Understanding Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and its evidence-based treatment approach developed by Dr. Ritchie Shoemaker.
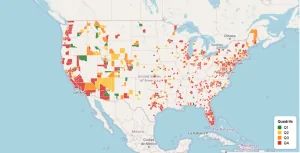
Indoor Heat Map
click here
Accreditation
External Resources
✕Preferred Specimen(s)
1 mL serum
Minimum Volume
0.5 mL
Transport Container
Transport tube
Transport Temperature
Refrigerated (cold packs)
Specimen Stability
Room temperature: Unacceptable
Refrigerated: 4 days
Frozen: 21 daysReject Criteria
Hemolysis • Grossly lipemic • Specimens with particulate matter or microbial contamination • Specimens outside of listed stability
✕Preferred Specimen(s)
1 mL serum
Minimum Volume
0.5 mL
Specimen Container
Plastic screw-cap vial
Transport Temperature
Frozen
Specimen Stability
Room temperature: 4 hours
Refrigerated: 24 hours
Frozen: 30 daysReject Criteria
Received room temperature • Gross hemolysis
✕Preferred Specimen(s)
1 mL plasma collected in an EDTA (lavender-top) tube
Minimum Volume
0.3 mL
Collection Instructions
Mix the sample and centrifuge immediately after collection to separate plasma from cells. Transfer plasma to a plastic specimen transport container and mark the specimen type as plasma on the container. Freeze immediately. Cytokine levels may demonstrate diurnal variation. Recommend cytokine levels be determined at the same time of day for improved longitudinal comparison.
Transport Container
Transport tube
Transport Temperature
Frozen
Specimen Stability
Room temperature: 4 hours
Refrigerated: 48
hours Frozen: 1 yearReject Criteria
Gross hemolysis • Gross lipemia • Received room temperature • Received refrigerated • Gross icterus
✕Preferred Specimen(s)
3 mL frozen plasma collected in an EDTA (lavender-top) tube
Minimum Volume
1 mL
Transport Container
Transport tube
Transport Temperature
Frozen
Specimen Stability
Room temperature: Unacceptable Refrigerated: Unacceptable
Frozen: 90 daysReject Criteria
Received room temperature • Received refrigerated
✕Preferred Specimen(s)
1 mL platelet-free plasma collected in EDTA (lavender-top) tube
Minimum Volume
0.25 mL
Collection Instructions
PSC Collections: Collect in EDTA (lavender-top) tube and immediately centrifuge to prepare platelet-poor plasma. Decant the plasma into another pour-over tube. Centrifuge a second time and pour over plasma. Freeze immediately.
Client Collections: Collect in EDTA (lavender-top) tube. Centrifuge for 15 minutes at 1000 X g within 30 minutes of collection. Centrifuge plasma again at 3000 X g for 10 minutes for complete platelet removal. Freeze Immediately.
For fixed speed centrifuges such as 645e: Collect in EDTA (lavender-top) tube. Centrifuge 3 times for 10 minutes at 1600 X g while decanting the plasma each time before the next spin within 30 minutes of collection. Freeze immediately.
Transport Container
Transport tube
Transport Temperature
Frozen
Specimen Stability
Room temperature: Not established
Refrigerated: 48 hours
Frozen -20° C: 14 days
Frozen -70° C: 30 daysReject Criteria
Hemolysis • Grossly lipemic • Specimens with particulate matter or microbial contamination • Specimens outside of listed stability